Annual inflation has dropped to 3.1%, but soaring food prices continue to strain household budgets despite the cooling economy.
Decreasing Inflation
Recently, annual inflation decreased to 3.1%, a figure that was higher than financial analysts had anticipated.
This indicates that while the overall rate of price increases across the economy is slowing down, it’s still happening at a pace that catches economists off guard.
Rising Cost of Food

A key driver behind this unexpected persistence of inflation is the rising cost of food, which continues to exert pressure on household budgets despite broader economic trends toward stabilization.
Impact of Food Prices on Inflation

The increase in grocery prices plays a significant role in the sustained high level of inflation despite a general trend of easing inflationary pressures.
This suggests that food costs remain a stubborn challenge even as inflation cools in other sectors of the economy.
Impacting Factors

The upward movement in grocery prices highlights the ongoing issue of food inflation and the impact of factors such as supply chain disruptions, agricultural conditions, and consumer demand on the cost of everyday essentials.
Acceleration in Prices

From December to January, there was a noticeable acceleration in grocery price increases, moving from a 0.1% rise to a 0.4% increase.
This shift illustrates the volatile nature of food inflation and its immediate impact on consumers, highlighting the challenges shoppers face in managing their grocery budgets amid fluctuating prices.
Staple Food Price Variation

Despite the overall easing of inflation, specific grocery items like bread, sugar, and juice continued to rise in price. At the same time, staples such as eggs, apples, and lettuce saw price decreases.
Yearly Comparison of Food Inflation

Comparing year-over-year data, the rate of increase in grocery prices has slowed to 1.2%, the lowest annual rate since June 2021 and a significant drop from the 13.5% surge seen in August 2022.
This trend suggests a gradual improvement in food inflation, offering some relief to consumers despite the ongoing pressure from high food costs.
Consumer Response to Price Changes

The article indicates varying consumer reactions to price adjustments, with reductions in the prices of staples like eggs, apples, and lettuce contrasted with increases in other items such as bread, sugar, and juice.
This differential pricing dynamic reflects the complexity of the grocery market, where price movements can vary widely across different categories of goods.
Historical Perspective on Grocery Prices
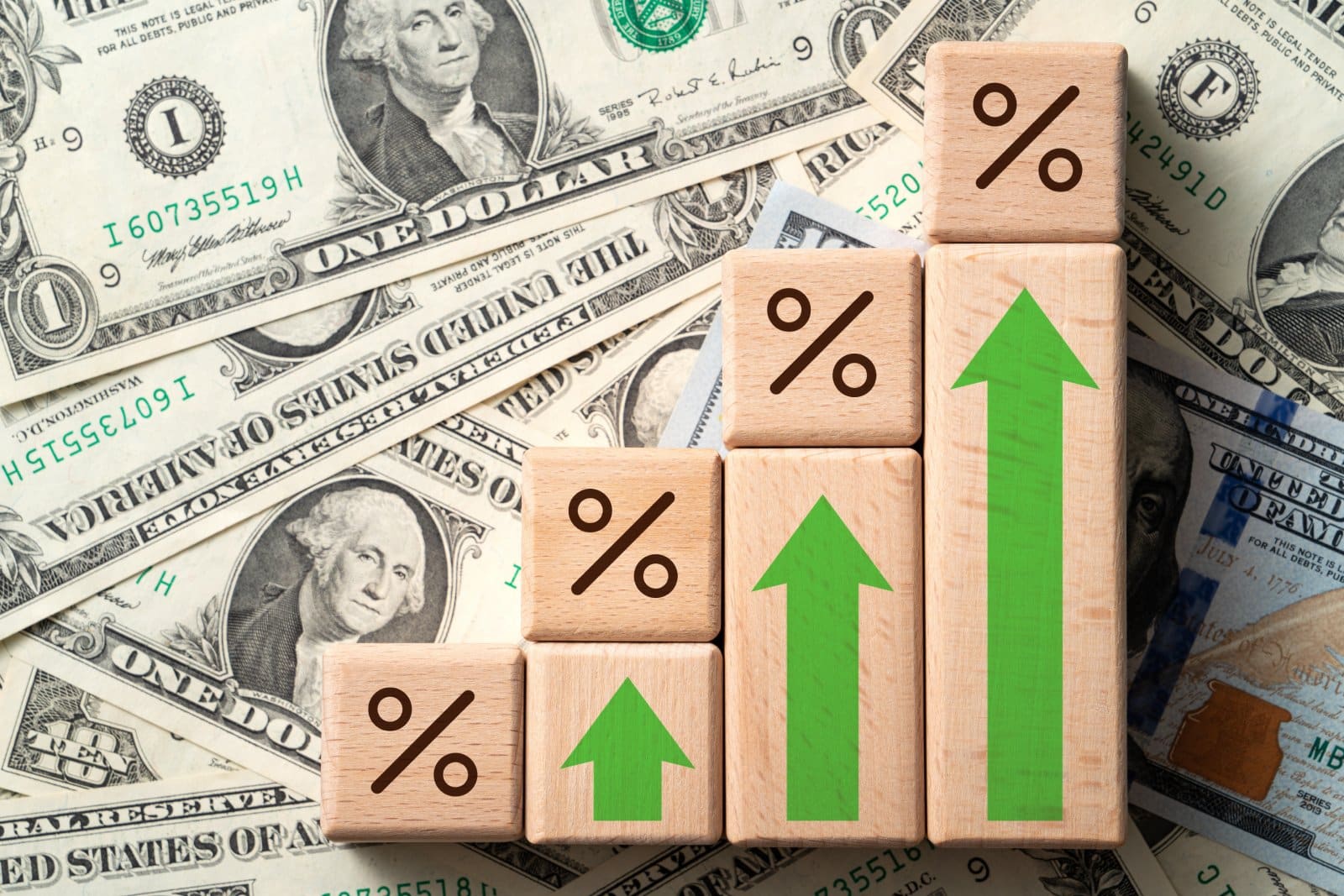

Since 2019, the cost of groceries has increased by 25%, rising faster than the overall rate of inflation. This statistic shows the significant burden placed on consumers by escalating food prices, contributing to widespread concern about inflation’s impact on the cost of living.
Public Concern and Policy Responses

A poll found that nearly 9 in 10 people are still concerned about inflation, with many viewing it as the country’s top issue.
This widespread concern has led to public criticism from figures such as President Joe Biden, who has attributed part of the blame for high food prices to corporate practices like “shrinkflation.”
Strategies and Outlook for Managing Inflation

While there are expectations for a slight decrease in grocery prices, the broader challenge remains in achieving a “soft landing” for the economy.
This involves slowing inflation without triggering a recession, a delicate balance that policymakers strive to achieve amidst complex economic conditions.
Regional Inflation
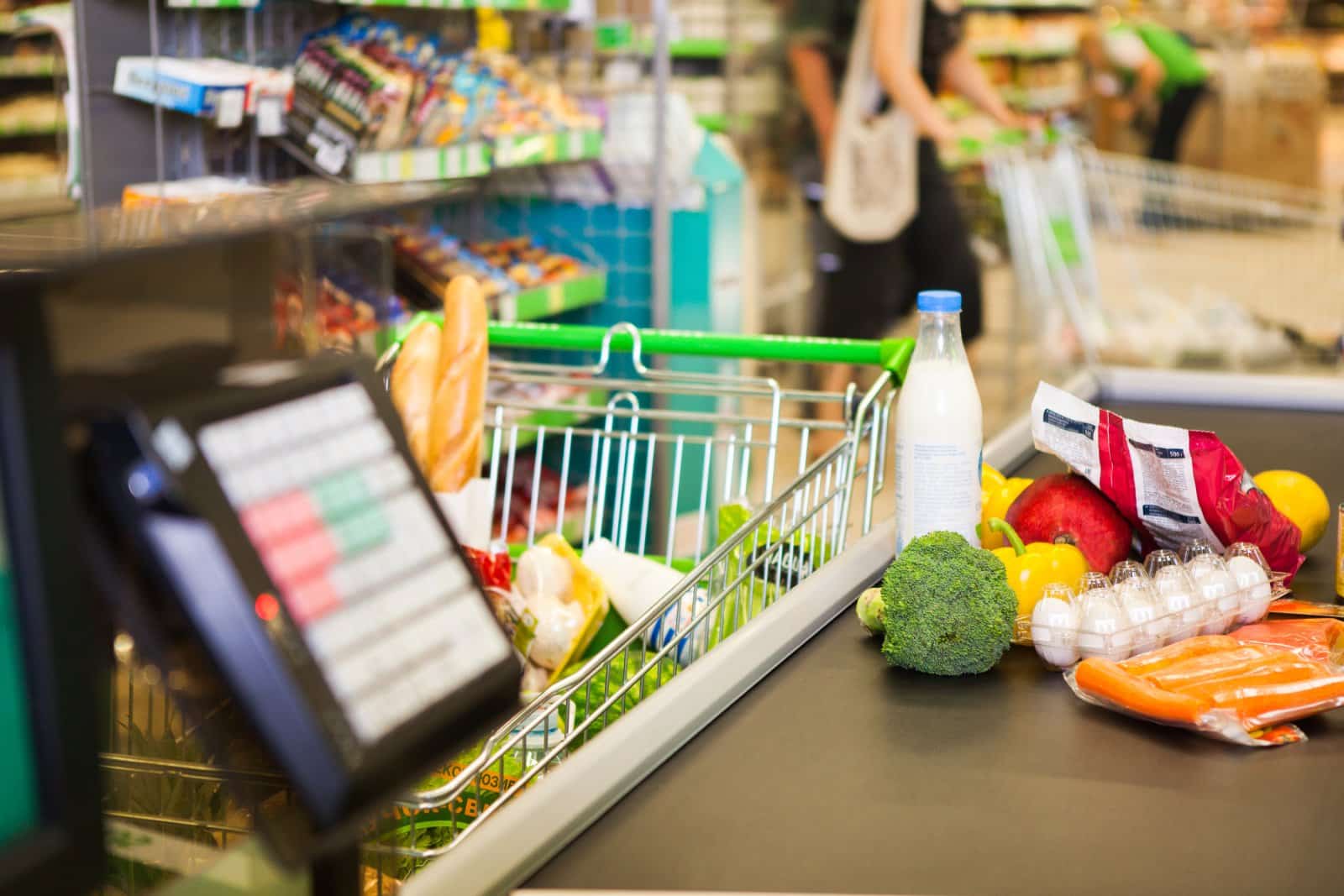

In Pennsylvania, residents experienced the highest grocery inflation rate in the country, with a notable 8.2% increase year-over-year.
This regional disparity makes the uneven impact of inflation across different areas clear, affecting consumer behavior and spending patterns as households adjust to higher food costs in different regions.
Economic Analysis and Future Projections

Despite the gradual cooling of inflation, U.S. households continue to face significant increases in their monthly expenses for everyday necessities.
This ongoing financial strain is reflected in rising wholesale inflation rates and core prices, indicating persistent inflationary pressures that may continue challenging economic stability and consumer welfare.
Political and Economic Discourse on Inflation

Amidst ongoing debates about the causes and solutions for inflation, President Joe Biden has pointed to corporate practices and high pricing strategies as contributing factors.
This critique forms part of a broader discussion on how to address inflation’s root causes and mitigate its impact on consumers, with a focus on ensuring fair pricing and protecting consumer interests in a fluctuating economy.
Ripping You Off
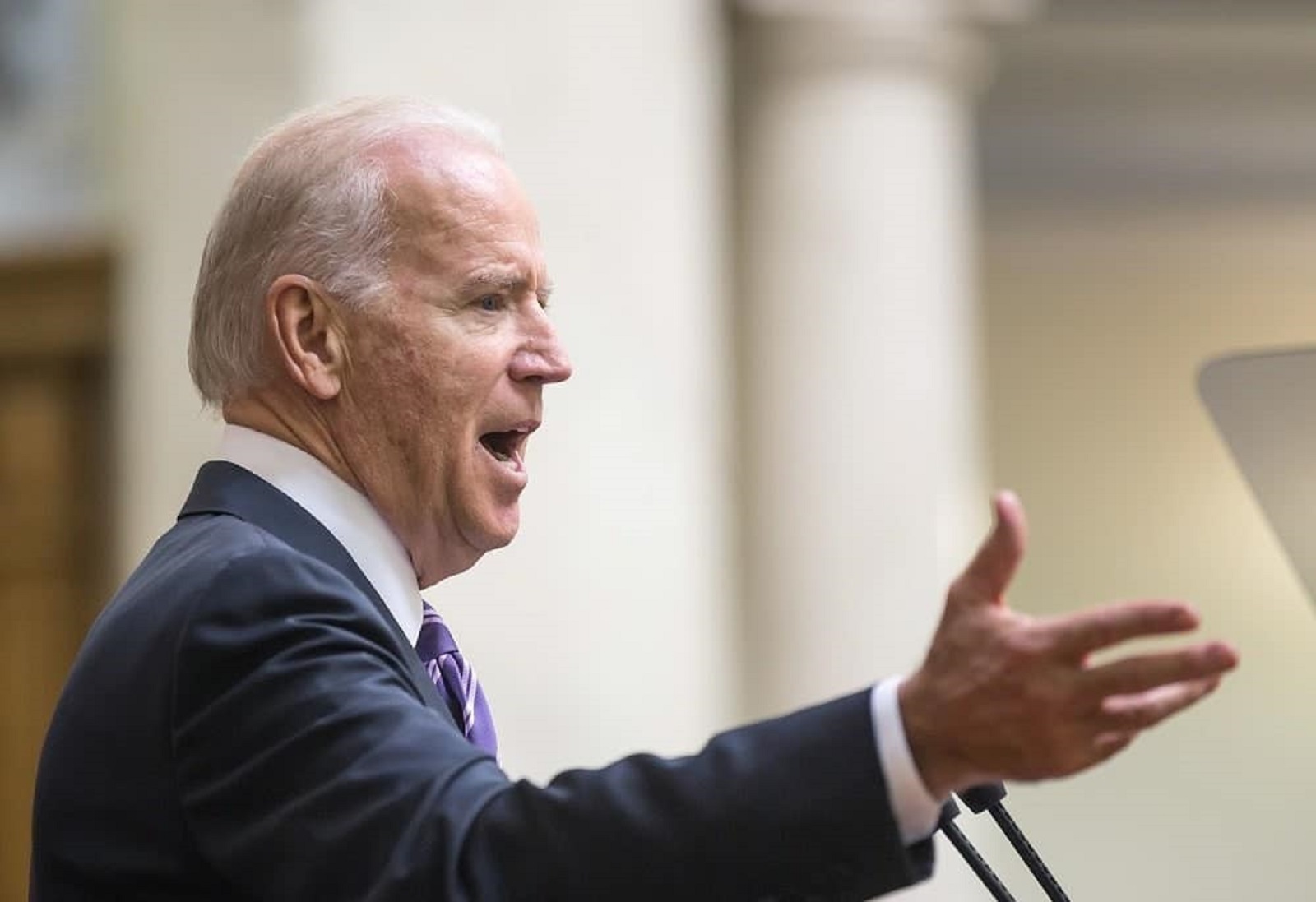

In his criticism, Joe Biden said, “for all we’ve done to bring prices down, there are still too many corporations in America ripping people off,” and “price gouging, junk fees, greedflation, shrinkflation.”
The post Biden Points Finger at Corporations for Rising Food Prices: Pennsylvania Hit Hardest first appeared on Swift Feed.
Featured Image Credit: Shutterstock / ZB Photos.

